Trauma from occlusion
What is trauma from occlusion?
Trauma from occlusion refers to the damage or injury caused to the teeth, jaw, or surrounding structures due to improper alignment or contact between the upper and lower teeth during biting or chewing.
What are the radiographic findings of trauma from occlusion?
- Fractured or Cracked Teeth: Radiographs can reveal fractures or cracks in the teeth resulting from occlusal trauma. These fractures may appear as visible lines or shadows within the tooth structure, often extending through the enamel, dentin, or even into the pulp.
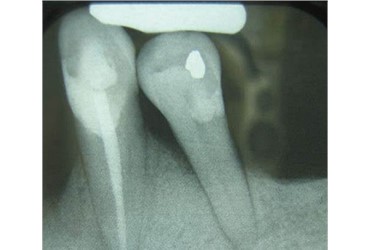
- Root Resorption: Trauma from occlusion can lead to root resorption, which is the loss or destruction of tooth root structure. Radiographs may show irregular or shortened roots, blunting of the root tips, or areas of root surface loss. Advanced cases of root resorption may even show complete loss of root structure.
- Widened Periodontal Ligament Space: The periodontal ligament is a thin space between the tooth root and the surrounding bone. Occlusal trauma can cause widening or thickening of this space due to increased forces exerted on the tooth. Radiographically, an enlarged periodontal ligament space may be seen as a dark, widened area around the root of the affected tooth.
- Alveolar Bone Loss: Chronic trauma from occlusion can result in bone loss around the affected teeth. Radiographs may reveal a loss of the normal bony contours around the teeth, indicating the presence of periodontal disease or bone resorption caused by occlusal trauma.
- Displaced Teeth: In cases of severe occlusal trauma, teeth may become displaced or intruded into the jawbone. Radiographs can help identify the altered position or abnormal angulation of the affected teeth.
- Pulpal Changes: Trauma from occlusion can cause damage to the dental pulp, resulting in inflammation or necrosis. Radiographs may show changes in the shape or size of the pulp chamber, indicating pulpitis or pulp necrosis.
What are the clinical findings of trauma from occlusion?
- Tooth Sensitivity: Patients may experience increased sensitivity or discomfort when biting or chewing, especially on specific teeth or areas of the mouth. The sensitivity may be temporary or persistent, depending on the extent of the trauma.
- Tooth Mobility: Trauma from occlusion can result in tooth mobility, where affected teeth may feel loose or exhibit slight movement when pressure is applied. The degree of mobility can range from mild to severe, depending on the severity of the trauma and the extent of supporting tissue damage.
- Tooth Wear or Chipping: Occlusal trauma can lead to excessive tooth wear or chipping. The teeth may exhibit flattened or worn biting surfaces, and there may be visible chips or fractures on the enamel. These findings can indicate that the teeth are experiencing excessive forces during biting or grinding.
- Occlusal Interference: Occlusal trauma can cause occlusal interferences, which are areas where the teeth do not meet properly during biting or chewing. These interferences may result in uneven distribution of forces, leading to discomfort, altered jaw movement, or difficulty in achieving a stable bite.
- TMJ (Temporomandibular Joint) Symptoms: Trauma from occlusion can contribute to temporomandibular joint dysfunction. Patients may experience jaw pain, clicking or popping sounds during jaw movement, limited jaw opening, muscle tenderness or fatigue, and headaches.
- Gingival inflamation: Chronic trauma from occlusion can affect the health of the surrounding gum tissues. Gingival recession, localized inflammation, or an increase in pocket depths (indicating periodontal disease) may be observed in the affected areas.
- Facial Pain or Muscle Tension: Some individuals with trauma from occlusion may experience facial pain, muscle tension, or discomfort in the jaw, cheeks, or temples. This can be associated with the increased strain on the masticatory muscles due to improper occlusal forces.
What are the common symptoms of trauma from occlusion?
Symptoms of trauma from occlusion can vary but may include tooth sensitivity, tooth mobility, tooth fractures or chips, jaw pain or discomfort, headaches, muscle tension, and difficulty in biting or chewing.
Is treatment necessary for trauma from occlusion?
Treatment for trauma from occlusion depends on the severity of the condition and its impact on the patient's oral health and quality of life. In some cases, minor occlusal adjustments or modifications in oral habits may be sufficient. However, more severe cases often require intervention to correct the occlusion and prevent further damage or discomfort.
What is the minimum treatment necessary to correct trauma from occlusion?
The minimum treatment necessary to correct trauma from occlusion depends on the specific situation and severity of the condition. In some cases, simple occlusal adjustments or bite splints may be sufficient to alleviate symptoms and prevent further damage. However, more complex cases may require orthodontic intervention, such as braces or aligners, to gradually align the teeth and improve occlusion. In severe cases, surgical correction may be necessary to realign the jaw and achieve optimal occlusion.
How can I determine the minimum treatment necessary for my trauma from occlusion?
It is essential to consult with a dental professional who specializes in occlusion and bite-related issues. They will evaluate your specific case through a comprehensive examination, which may include dental scans, X-rays, and analysis of your dental and medical history. Based on this evaluation, they will be able to recommend the minimum treatment necessary to correct your trauma from occlusion and achieve optimal oral health and function.
Are there any non-invasive or conservative treatment options available for trauma from occlusion?
Yes, there are non-invasive or conservative treatment options available for trauma from occlusion. These may include occlusal adjustments, where the dentist makes minor modifications to the biting surfaces of the teeth to achieve better alignment. Additionally, the use of bite splints or nightguards can help alleviate symptoms and protect the teeth from further damage caused by grinding or clenching.
How long does the treatment for trauma from occlusion typically take?
The duration of treatment for trauma from occlusion varies depending on the severity of the condition and the chosen treatment approach. Minor occlusal adjustments or conservative treatments may require fewer visits and a shorter treatment time. Orthodontic interventions, such as braces or aligners, can take several months to a few years, depending on the complexity of the case. Surgical correction may involve a longer treatment timeline, including a recovery period.